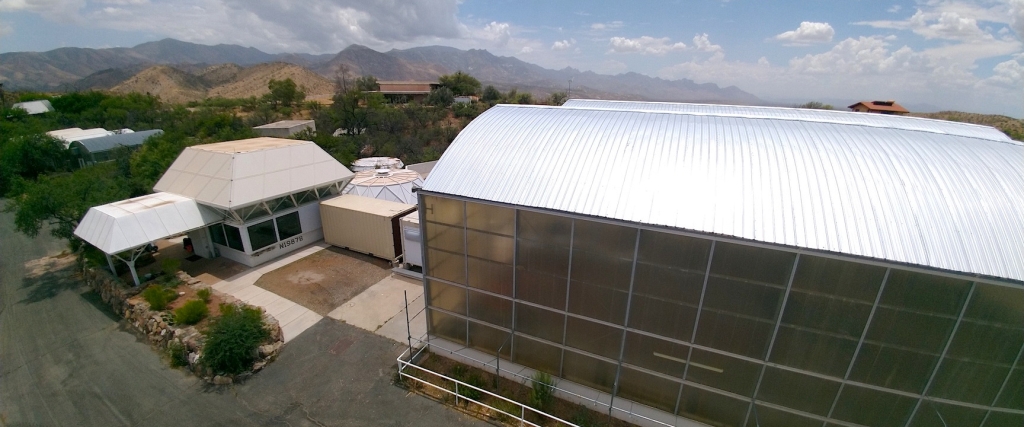
Back to the grind(ing wheel)
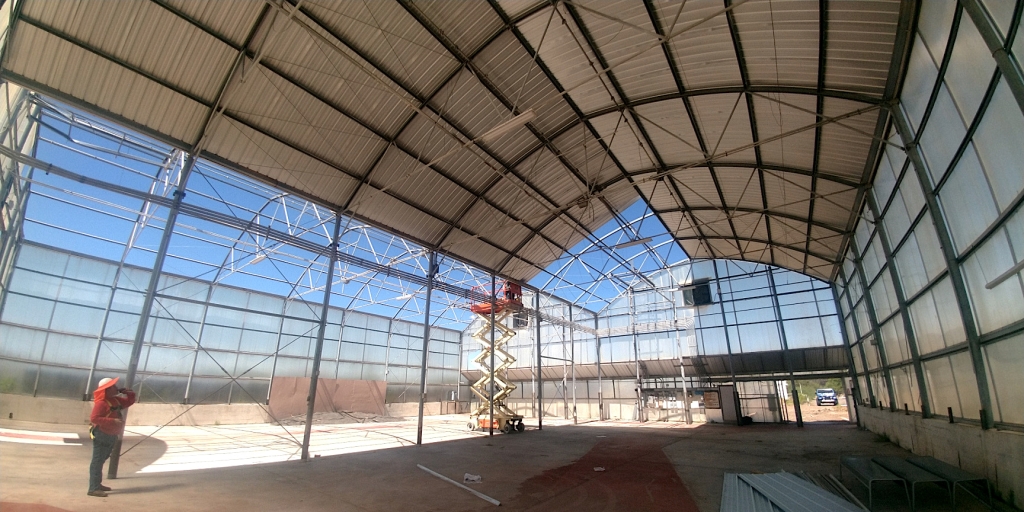
With the daytime temperatures quite comfortable and the SAM team fully recovered from the last construction sprint, we are back to SAM with a singular focus — achieve a hermetic seal and hold an internal, positive pressure for as long as possible.
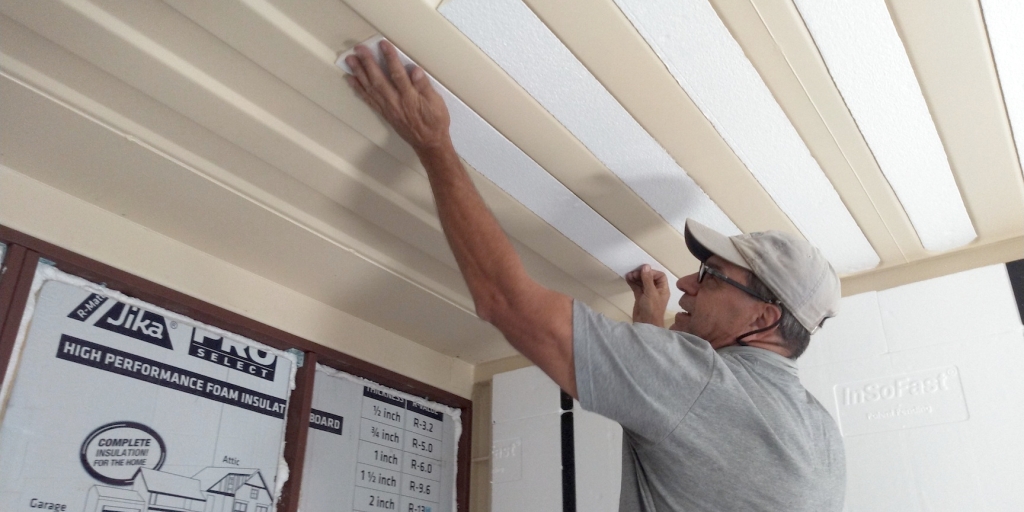
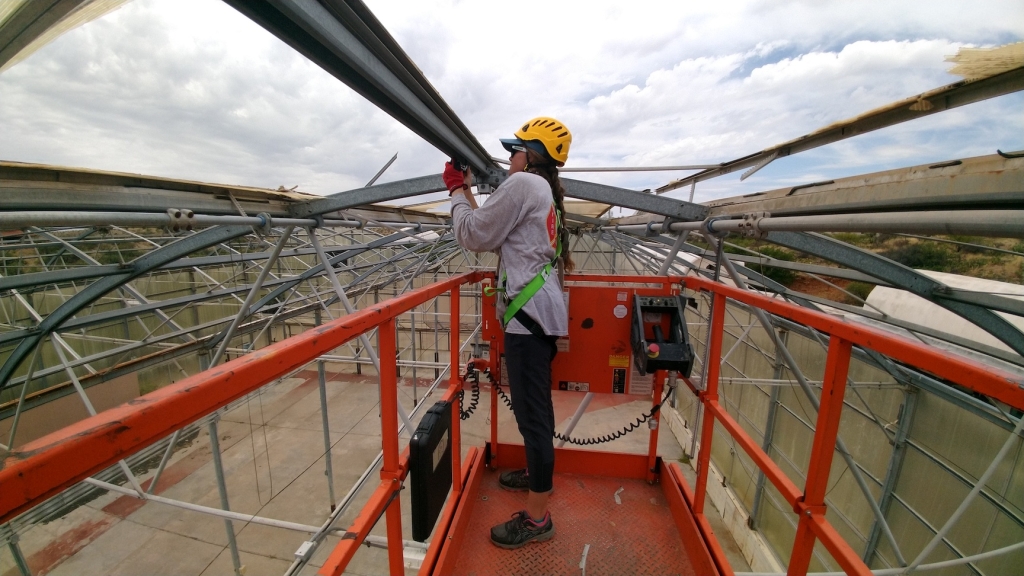
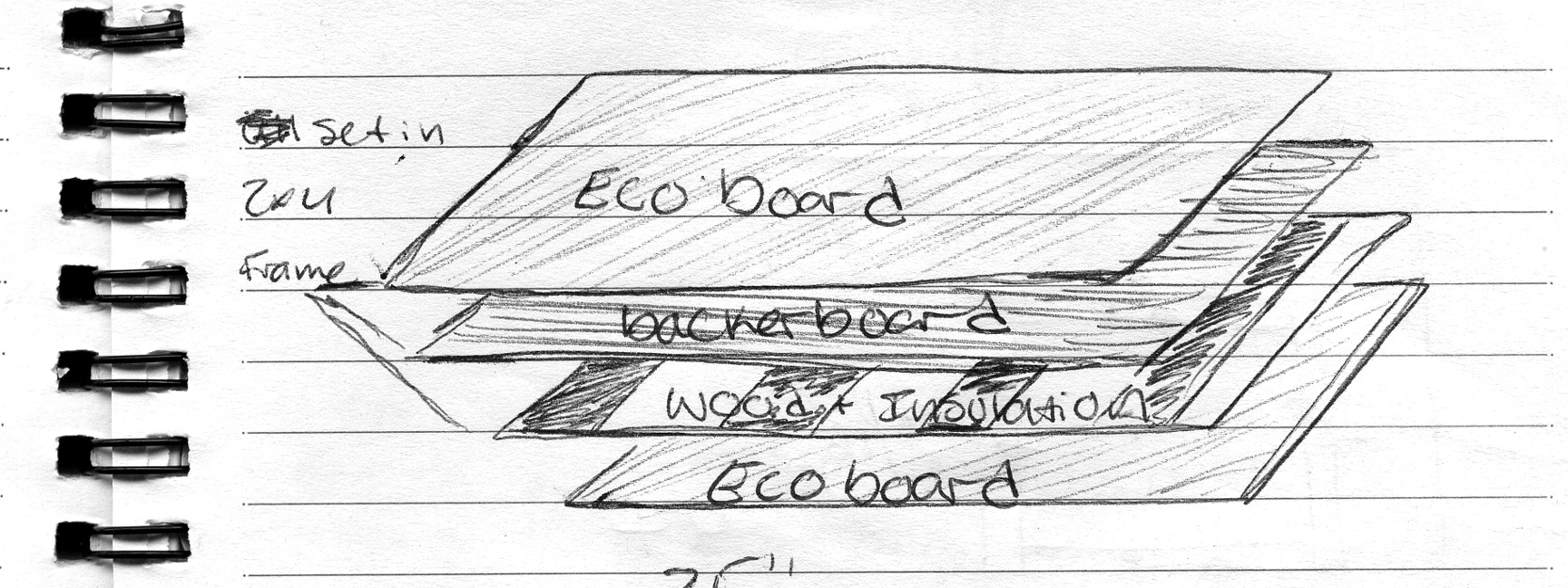
To this end, every sheet metal screw that extends from inside to out is backed out of its threads, coated with 795 silicon, and seated again. All temporary silicon finger beads will be replaced with silicon channels or welding to minimize the gas transmission over time. The final rows of insulation in the 20′ shipping container (SAM workshop) are being completed, a job unfinished from the final days of our effort in July.
This is the best part of a multi-year endeavor, when the team has worked together through thick and thin, through snowfall and in the blazing sun, success, failures, and everything in between—all project segments that lie ahead are well defined and each week we feel we are making progress toward the goal of providing a hi-fidelity research vessel for visiting, research teams.
We are eager to conduct our first pressure test since June 29, 2021!